Abstract
Background:
Multiple Myeloma (MM) is a progressive plasma cell neoplasm characterized by heterogeneous clonal expansion. Despite numerous targeted therapy options, failing anti-BCMA CAR-T cell therapy represents a challenging treatment course with dismal prognosis. 53% of relapsed/refractory (rr) MM patients have shown emerging clones harboring mutations within the MAPK signaling pathway including the targetable BRAF V600E in 7% of cases. Allosteric kinase inhibition of MAPK pathway with BRAF monomer selective inhibitors +/- MEK inhibitor have been frequently attempted with rrMM patients with equivocal outcome on both disease progression and survival. This could be ascribed to the feedback activation of the pathway via BRAF dimers induction. In solid tumor contexts, a recent study has revealed that the multi-kinase inhibitor regorafenib is a potent and selective inhibitor of dimeric BRAF. Moreover, the study demonstrated overcoming of this negative feedback by combining two inhibitors targeting BRAF in its monomeric and its dimeric form, respectively, with MEK inhibition leading to more efficacious and tolerable treatment (Adamopoulos C. et al. Cancer Discov. 2021). Here, we show the applicability, effectiveness, and tolerability of the aforementioned triple therapy strategy in hematological malignancy context to salvage post BCMA CAR-T cell therapy in a BRAF V600E rrMM patient.
Material and Methods:
CD138 + selected cells were collected from bone marrow (BM) and patient's plasmacytoma before and after CAR-T cell therapy relapse, respectively. Samples were processed using the standard GATK 4 workflows and a consensus mutation calling approach was used to call somatic mutations using a matched normal obtained from peripheral blood. PhyloWGS (Deshwar et al, Genome Biol 2015) was then used to perform intra-tumor heterogeneity modeling and phylogeny estimation.
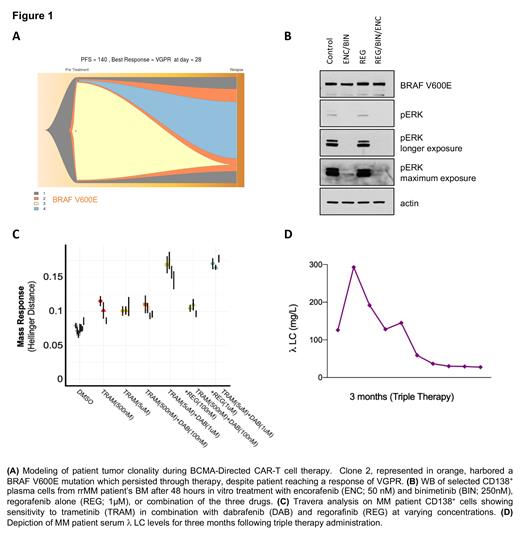
CD138 + selected cells from BM of rrMM patient were treated with encorafenib (50nM) and binimetinib (250 nM) +/- regorafinib (1mM) for 48 hours, cells were harvested, lysed and immunoblotted with BRAF V600E and pERK antibodies.
In parallel, rrMM patient BM selected CD138 + cells' sensitivity to MAPK inhibitors were assessed by Travera. Cells are incubated with different inhibitors at varying concentrations and combinations for 15 hours before having their single-cell mass distributions measured. Sensitivity is then characterized by the relative statistical difference (Hellinger distance) between conditions and untreated controls.
A rrMM patient was started on targeted triple therapy using the following combination: BRAF monomer-inhibitor, dabrafenib (100mg, orally twice daily), a MEK-inhibitor, trametinib (1.5mg, orally for 21/28 days daily), and a BRAF dimer inhibitor, regorafenib (40mg, orally once daily).
Results:
Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) showed a BRAF V600E mutation was present prior to CAR-T cell therapy and persisted through subsequent treatments. The variant allele frequency of the mutation was 41% post CAR-T cell therapy (Figure 1A).
Western blot of CD138 + cells confirmed BRAF V600E mutation with a specific antibody, and showed ERK phosphorylation, which was inhibited with trametinib. Longer exposure to trametinib confirmed a feedback loop activating MAPK which was abrogated with the BRAF dimer inhibitor regorafenib (Figure 1B).
Travera analysis showed CD138 + cells' sensitivity to the combination of trametinib at 5mM, and dabrafenib at 1µM. Adding regorafenib at 1µM could slightly improve the response compared to the double combination. (Figure 1C).
Clinically, three months of the triple therapy administration has led to prompt reduction in subcutaneous skin lesions as well as 80% reduction in free lambda chain (Figure 1D). Furthermore, the patient exhibited good tolerance to all three medications with minimal side effects (grade 1 fatigue). The treatment regimen allowed the patient to carry out activities of daily living and resume work.
Conclusion:
We have shown the applicability, effectiveness, and tolerability of the triple MAPK inhibition in a hematological malignancy context to salvage post BCMA CAR-T cell therapy in a rrMM patient with BRAF V600E mutation. Also, we have revealed the power of routine WES in tracking clonal evolution, and identifying targetable mutations which allows tailoring of therapeutics for MM patients.
Stevens: Travera: Current Employment. Parekh: Foundation Medicine Inc: Consultancy; Amgen: Research Funding; PFIZER: Research Funding; CELGENE: Research Funding; Karyopharm Inv: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal